SparingVision’s second product, SPVN20, is a pioneering gene therapy product obtained through the acquisition of Gamut Therapeutics in 2021.
SPVN20’s unique gene agnostic approach aims to restore visual acuity and color vision in advanced and late-stage Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP) patients with “dormant cones”, independently of their genetic mutation.
Description
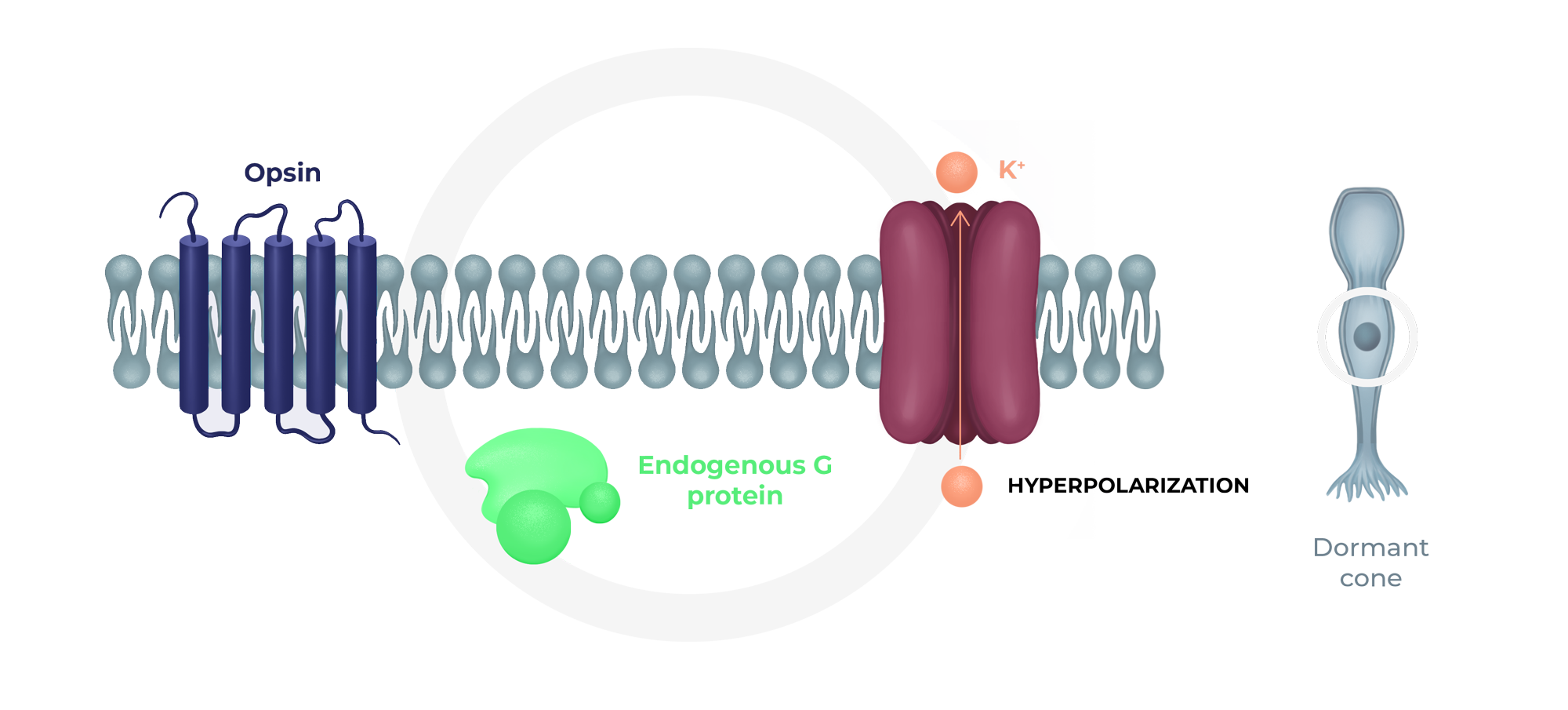
SPVN20 aims to reactivate patients’ “dormant cones”.
Dormant cones are viable cones with diminished outer segments that no longer respond to light, as such that the patients’ light response decrease and they become unable to see. Since the phototransduction cascade (which allows for normal vision) occurs in the outer segment of the cones, these dormant cones are no longer capable of converting light into an electric signal, leaving patients with tunnel vision and, as the disease progresses, ultimately blindness.
Phototransduction cascade in normal vision
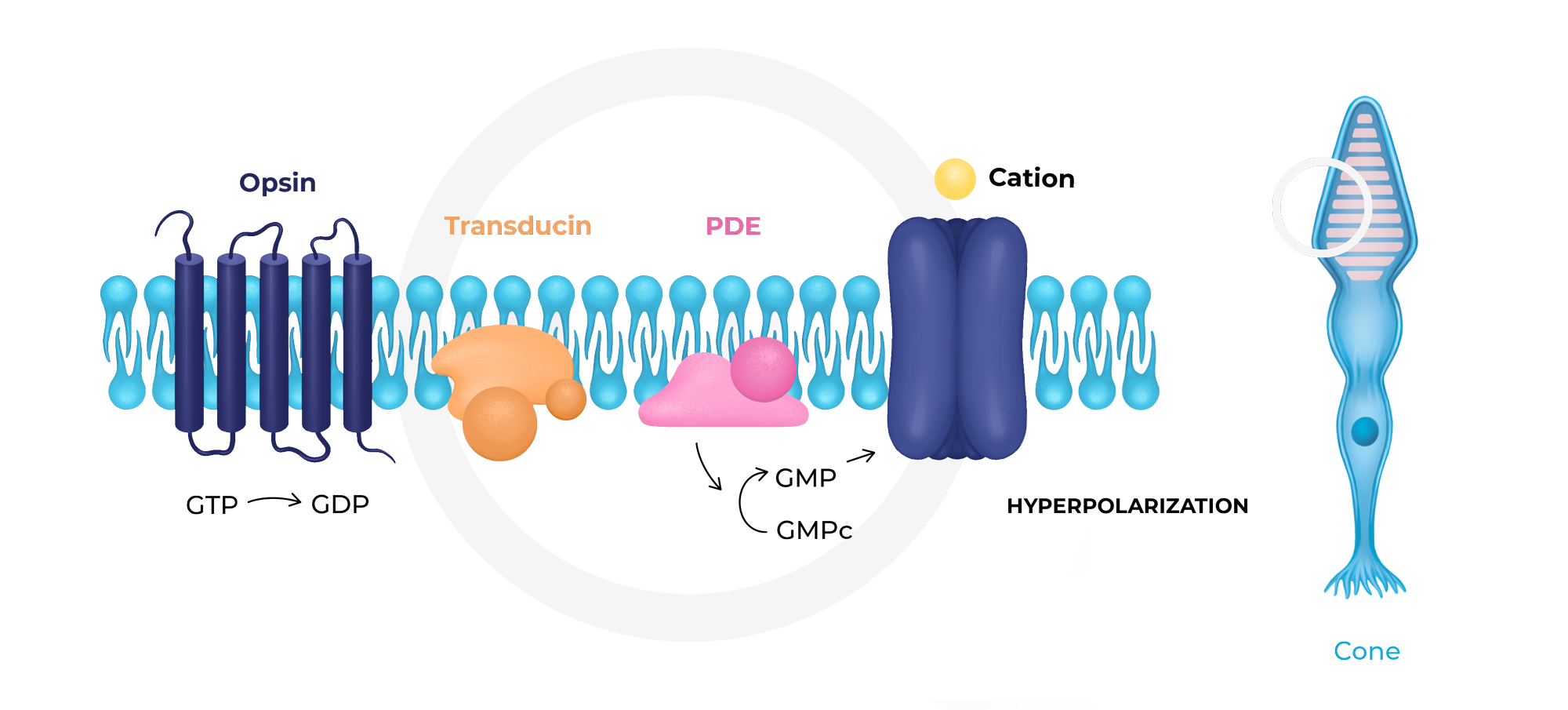
Injection with SPVN20 provides dormant cone cell bodies with a channel protein that would allow to restore a short phototransduction cascade within the dormant cone, restoring electric signal and thereby visual acuity and color vision.
Short phototransduction cascade with SPVN20
Development plan
The addition of SPVN20 in March 2021 broadened SparingVision’s novel genomic medicine pipeline. SPVN20 is expected to enter the clinic in 2024, with first safety and activity data expected in 2025. Beyond RP, SparingVision will explore opportunities to evaluate SPVN20 in other IRDs, where its mechanism of action could be particularly relevant.
SPVN30
SparingVision also intends to evaluate the potential therapeutic synergy of its two lead products through the combination of SPVN06 and SPVN20 as a single construct, called SPVN30, to address a broader population of Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP) patients.
Publications
Vertebrate cone opsins enable sustained and highly sensitive rapid control of gi/o signaling in anxiety circuitry
Masseck, O. A., Spoida, K., Dalkara, D., Maejima, T., Rubelowski, J. M., Wallhorn, L., …Herlitze, S. (2014).
Neuron, 81(6), 1263–1273.
Crystal structure of the mammalian GIRK2 K +channel and gating regulation by G proteins, PIP 2, and sodium
Whorton, M. R., & MacKinnon, R. (2011)
Cell, 147(1), 199–208.
X-ray structure of the mammalian GIRK2-βγ Gprotein complex
Whorton, M. R., & MacKinnon, R. (2013)
Nature, 498(7453), 190–197.









